Clean Up Your Digital Life: How I Found 1929 Fully Identical Images, Dark, Bright and Blurry Shots in Minutes, For Free.




Table of Contents
Table of Contents
✅ Motivation
In today’s world of selfies and Instagram, we all take tons of photos on our phones, cameras, and other gadgets.
But let’s be real, it’s easy for our photo collections to become a chaotic mess, making it impossible to find that one special memory.
I mean, I’ve got gigabytes of photos on my Google Photo app filled with dark shots, overly exposed shots, blurry shots, and tons of duplicate stills.
And let’s face it, what we post on Instagram vs what’s behind the scenes can be wildly different.

Me vs my photo album.
I know, you’ll say that there’s no harm in keeping those extra selfies in your phone. Right?
Not in the short term. But over time, these photos will just clutter your devices taking up valuable disk space and slowing down your device.
Also, think about these -
- It’s difficult to find specific photos when your collection is in a mess.
- Organizing your collection saves you time spent searching for photos.
- An organized photo collection can be a source of pride especially when you share them.
- Digital clutter not only affects your device but also impacts you psychologically.
So consider cleaning up your digital clutter, because it pays in the long run.
If you’re convinced, now comes the next hurdle.
Spending hours sorting through your photos and cleaning them is a pain. Nobody has time for that. We’re busy people.
Don’t fret, that’s what this post is about. In this post, I’ll show you how to tidy up your digital life by organizing your photo collection and not spending an entire weekend doing it.
tip
💫 Here’s what you’ll learn by the end -
- How to isolate corrupted images in your photo album.
- How to identify duplicates in your photo album.
- How to filter out photos that are too dark, too bright, or blurry.
- How to cluster similar-looking shots together.
- How to bulk-delete photos.
📝 NOTE: All codes used in the post are on my Github repository.
⚡ fastdup
fastdup is a tool that let you gain insights from a large image/video collection.
You can manage, clean, and curate your images at scale on your local machine event with a single CPU. fastdup lets you clean visual data with ease, freeing up valuable resources and time.
Here are some superpowers you get with fastdup - it lets you identify:

fastdup superpowers. Source: fastdup GitHub.
In short, fastdup is 👇
- Unsupervised: fits any visual dataset.
- Scalable: handles 400M images on a single machine.
- Efficient: works on CPU (even on Google Colab with only 2 CPU cores!).
- Low Cost: can process 12M images on a $1 cloud machine budget.
🌟 The best part? fastdup is free.
info
fastdup also offers an Enterprise edition of the tool that lets you do more. Find out here.
If that looks interesting, let’s get started with.. 👇
☕ Messy Images

As we are going to clean up messy albums, the first step is to download the photos from your Google Photos, Onedrive, or whatever cloud service you use into your local drive.
I don’t have a massive photo collection, so I’ll be using an image collection from Kaggle that was scraped off Google Images.
The contributor Debadri Dutta has a knack for photography and traveling. A lot of the images from the collection are uploaded by users on social media. So I thought it would be a good fit to use it for this post.
Here are a few sample images.
Sample images scraped from Google.
With the images downloaded locally let’s organize them in a folder. Here’s how the folders look on my computer.
├── images
| ├── image001.jpg
| ├── image002.jpg
| └── ...
├── fastdup_report
└── fastdup_analyze.ipynb
note
Description -
images/– Folder to store the images.fastdup_report/– Directory to save the output generated by fastdup.fastdup_analyze.ipynb– Jupyter notebook to run fastdup.
📝 NOTE: If you’d like to follow along with the example on this post download the images to your desktop from Kaggle here into the images/ directory.
With the folders in place let’s get working.
🧮 Install and Run
First, let’s install fastdup with:
pip install fastdup
I’m running fastdup==0.903 and Python 3.10 for this post.
Feel free to use the latest version available.
After the installation completes, you can now import fastdup in your Python console and start the run.
import fastdup
work_dir = "./fastdup_report"
images_dir = "./images"
fd = fastdup.create(work_dir, images_dir)
fd.run()
note
images_dir– Path to the folder containing images.work_dir– Path to save the outputs from the run.
📝 NOTE: More info on other parameters on the docs page.
This starts the process of detecting all issues on the images in images_dir.
Depending on your CPU power, this may take a few seconds to a few minutes to complete.
On my machine, with an Intel Core™ i9-11900 it takes under 1-minute to check through (approx. 35,000) images in the folder 🤯.
Once the run completes, you’ll find the work_dir populated with all files from the run.
tip
fastdup recommends running the commands in a Python console and NOT in a Jupyter notebook.
Personally, I find no issues running the commands in a notebook. But beware that the notebook size can be large especially if there are lots of images rendered.
Once the run is complete, we can visualize the issues.
For a summary, run
fd.summary()
Here are some useful information from the summary.
- Dataset contains 35136 images.
- Valid images are 99.83% (35,077) of the data, invalids are 0.17% (59) of the data'
- 2.15% (756) belong to 12 similarity clusters (components).
- Largest cluster has 16 (0.05%) images.
- 6.16% (2,163) of images are possible outliers, and fall in the bottom 5.00% of similarity values.
There are a few issues we can already spot there but let’s start with 👇
🚫 Invalid Images
Invalid images are files that cannot be read by fastdup. Chances are, they are corrupted images.
We have 59 of them according to the summary. To get the list of invalid images, run:
fd.invalid_instances()
which outputs
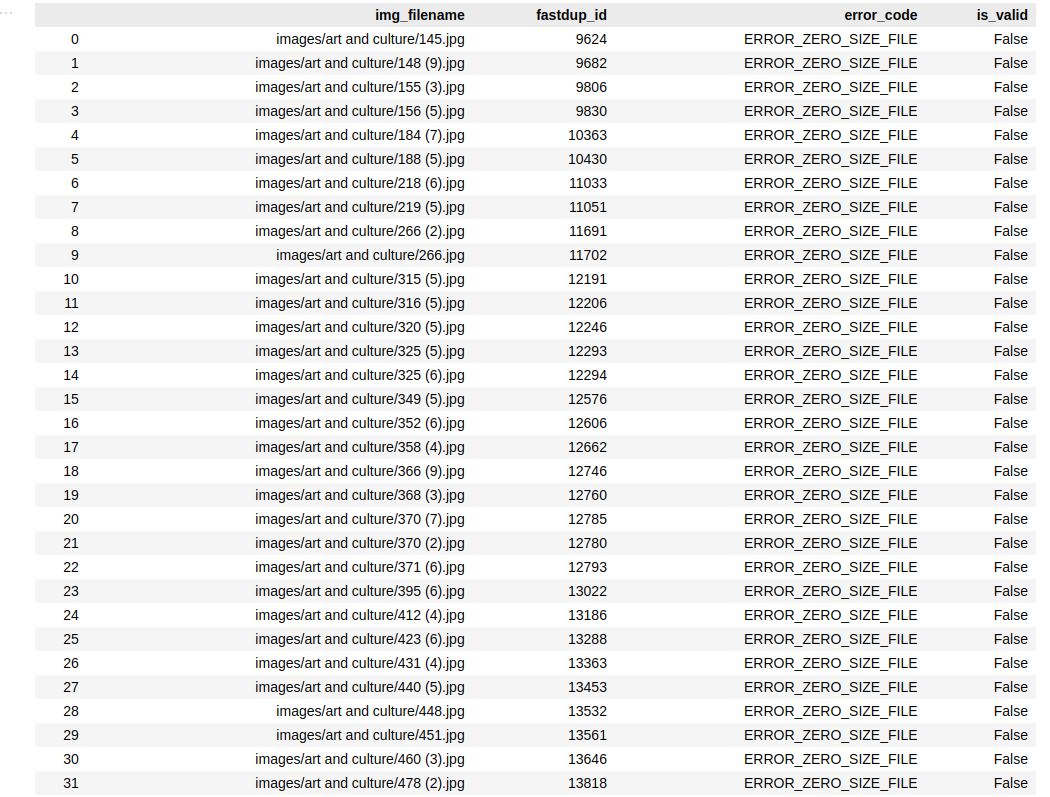
I tried to open these images on my machine, but they could not be viewed.
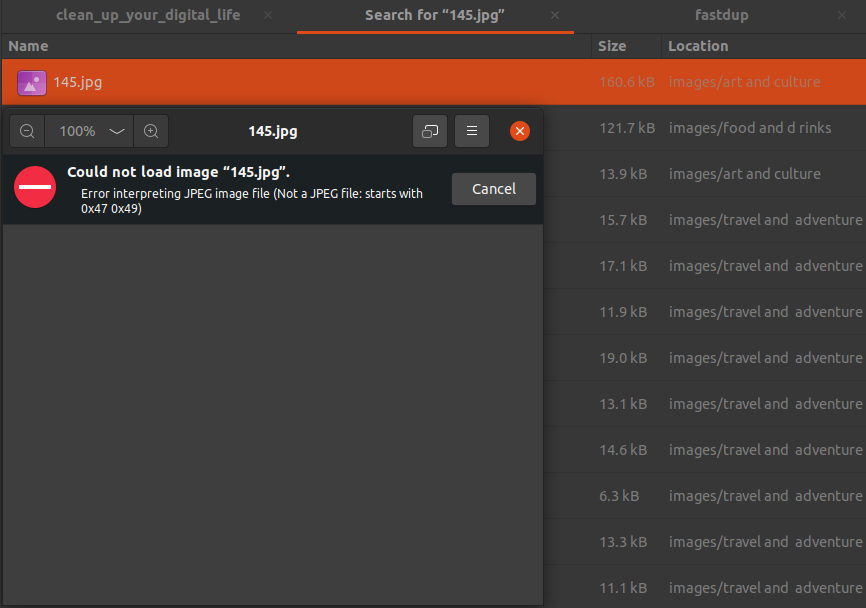
Invalid images can’t be used but take up disk space. There’s only one way to deal with it - Delete.
To delete corrupted images with fastdup, let’s collect the images into a list:
invalid_images = fd.invalid_instances()
list_of_invalid_images = invalid_images['img_filename'].to_list()
images_to_delete now contains a list of file directories to be deleted.
['art and culture/145.jpg',
'art and culture/148 (9).jpg',
'art and culture/155 (3).jpg',
'art and culture/156 (5).jpg',
...
...
...
'art and culture/98 (5).jpg',
'food and d rinks/1.jpg',
'food and d rinks/28 (2).jpg',
'food and d rinks/325 (3).jpg',
'food and d rinks/424.jpg']
What’s left to do next is to write a function to delete images in list_of_invalid_images.
warning
The following code will DELETE ALL corrupted images specified in list_of_invalid_images.
I recommend making a backup of your existing dataset before proceeding.
from pathlib import Path
def delete_images(file_paths):
for file_path in file_paths:
path = images_dir / Path(file_path)
if path.is_file():
print(f"Deleting {path}")
path.unlink()
And call the function:
delete_images(list_of_invalid_images)
Just like that, we’ve deleted all corrupted images from our dataset!
tip
You can optionally choose to move the images to another folder instead of deleting them like what we did above.
We can do that with the following function:
import shutil
from pathlib import Path
def move_images_to_folder(file_paths, folder_name="invalid_images"):
corrupted_images_dir = Path(folder_name)
corrupted_images_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True) # create the directory if it doesn't exist
for file_path in file_paths:
path = images_dir / Path(file_path)
if path.is_file():
new_path = corrupted_images_dir / Path(file_path)
new_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # create the parent directory if it doesn't exist
print(f"Moving {path} to {new_path}")
shutil.move(str(path), str(new_path))
And call the function:
move_images_to_folder(list_of_invalid_images)
This should move the invalid images into the folder_name directory.
👯♂️ Duplicate Images
To view the duplicate photos run:
fd.vis.duplicates_gallery()
If you’re running this in a Jupyter notebook, you’ll see something like the following.
A generated gallery of duplicates.

note
You can optionally specify num_images – The max number of images to display. Defaults to 20.
📝 NOTE: More info on other parameters here.
In the visualization above we see that there are exact copies residing in different folders within the images_dir.
So what do we do about it? You can either refer to the file name and delete the duplicate images by hand.
Or
Use a convenient function in fastdup to bulk delete images that are EXACT copies.
To do that, let’s first get the connected components DataFrame:
cc_df, _ = fd.connected_components()
Next, we will group the connected components DataFrame to show only the duplicates:
def get_clusters_of_duplicates(df, sort_by='count', min_count=2, ascending=False):
agg_dict = {'img_filename': list, 'mean_distance': max, 'count': len}
df = df[df['count'] >= min_count]
df = df[df["mean_distance"]==1.0]
grouped_df = df.groupby('component_id').agg(agg_dict).sort_values(by=[sort_by], ascending=ascending)
return grouped_df
duplicates_df=get_clusters_of_duplicates(cc_df)
In duplicates_df you’ll now find:
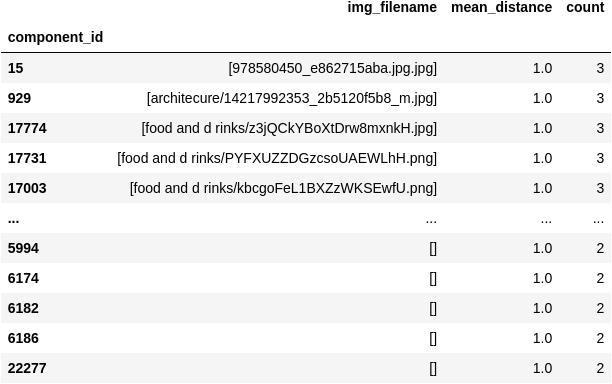
Now let’s turn the contents of duplicates_df into a list of images using the function:
def get_list_of_duplicate_images(df):
df['img_filename'] = df['img_filename'].apply(lambda row: row[1:])
# Get a list of images to delete from the df
list_of_duplicate_images=duplicates_df['img_filename'].to_list()
# Flatten list
list_of_duplicate_images = [item for sublist in list_of_duplicate_images for item in sublist]
return list_of_duplicate_images
Calling the function
list_of_duplicate_images = get_list_of_duplicate_images(duplicates_df)
We end up with list_of_duplicate_images
['978580450_e862715aba.jpg.jpg',
'architecure/14217992353_2b5120f5b8_m.jpg',
'food and d rinks/z3jQCkYBoXtDrw8mxnkH.jpg',
'food and d rinks/PYFXUZZDGzcsoUAEWLhH.png',
'food and d rinks/kbcgoFeL1BXZzWKSEwfU.png',
'food and d rinks/pIX6YKvYX2sJcgAk5aCo.jpg',
..
..
..
'architecure/11543398565_7a25482b20.jpg',
'food and d rinks/uO6H0sqpkRdg20J3QvzX.jpg',
'food and d rinks/zxN445iYMYExleeeKhA6.jpg']
With this you can use the functions move_images_to_folder or delete_images we defined earlier.
Just like that, we’ve eliminated duplicates from the album! In this post, I found a total of 1929 fully identical images!
Now on to the next common problem in photo albums 👇
🤳 Dark, Bright, and Blurry Shots
Let’s be real, even pros have overly dark bright, and blurry shots in their albums. These shots are probably not going to be used and hog your storage space.
With fastdup you can filter them out with:
fd.vis.stats_gallery(metric='dark')
The above snippet sorts all the photos in your folder following ascending mean values. So the darker images (lower mean value) should appear at the top.

A generated gallery of dark images.
The first 3 images (totally black) are classic. I always find these somewhere in my albums due to accidental press when the phone is in my pocket.
I leave it to you to judge if you’d keep or discard the rest of the images.
Conversely, get the brightest images on top with:
fd.vis.stats_gallery(metric='bright')

A generated gallery of bright images.
Again, see the first 3 images (totally white) which happens sometimes when your shots are overexposed.
And next, let’s sort our album with the blur metric.
You’ve guessed it, this sorts our album with the most blurry image on top.
fd.vis.stats_gallery(metric='blur')

A generated gallery of blur images.
There are more ways we can view our photos using statistical metrics. So you can change the metric argument to:
blur– Sort by blurriness.mean– Sort by mean value.min– Sort by minimum value.max– Sort by maximum value.stdv– Sort by standard deviation value.
View other examples here.
tip
Try running with metric='stdv'. You’ll find images that lie outside of the standard deviation and potentially find anomalies in them.
🗂 Clustering Similar Shots
This is one of my favorite functions in fastdup.
With all the thousands of photos in one album, it will be interesting to group similar shots to assess them as a whole.
It’s also easier to identify patterns and trends in these similar shots. Or you may find that these shots are just redundant shots that will not be used.
To group similar shots together run:
fd.vis.component_gallery()
And you’ll find something like the following.

Above, I’ve shown you three examples of similar-looking shots grouped together with the file path of each image. It’s up to you to decide what to do with the similar-looking shots. Not going to use them? Delete. Otherwise, you can also keep them organized in a folder of some sort.
tip
Check out the full output of the above code in the notebook.
🔓 Conclusion
Cleaning up your digital photo collection is an important step towards simplifying your digital life.
Disorganized photos can take up valuable storage space, slow down your device’s performance, and make it difficult to find specific photos when you need them.
In this blog post, I’ve shown you how to use fastdup to programmatically clean your photo collections without spending a lot of time.
tip
💫 Here’s what we learned -
- How to identify duplicates in your photo album using Python code.
- How to filter out photos that are too dark, too bright, or blurry.
- How to group similar-looking shots together.
- How to bulk-delete photos.
📝 NOTE: All codes used in the post are on my Github repository.
By using fastdup to identify and delete duplicate and unwanted photos, and clustering similar photos for easy organization, you can save time and energy and enjoy a well-organized digital photo collection.
I hope you’ve enjoyed and learned a thing or two from this blog post. If you have any questions, comments, or feedback, please leave them on the following Twitter/LinkedIn post or drop me a message.
Cleaning image datasets is painful, esp if your dataset is huge.
— Dickson Neoh 🚀 (@dicksonneoh7) January 26, 2023
If you find yourself sifting through images for duplicates and anomalies, you're not alone. I've been there. 😭
I'll show how you can inspect large image dataset efficiently for free.
A 🧵 pic.twitter.com/2J4W6GF4fy

